Valance Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR Theory)
Concern
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory abbreviated as VSEPR theory is based on the premise that there is a repulsion between the pairs of valence electrons in all atoms, and the atoms will always tend to arrange themselves in a manner in which this electron pair repulsion is minimalized. This arrangement of the atom determines the geometry of the resulting molecule.
Important points:
- VSEPR theory predicts the shape of molecules or ions based on the arrangement of the valance shell electron pair around the central atom.
- Electron Pair = Bond Pair + Lone Pair
- According to VSEPR Theory, valance shell electron are arranged around the central atom such that the repulsion between them becomes minimum.
- according to VSEPR Theory repulsion between electron pair is
L.P.--L.P. > L.P--B.P. >B.P.--B.P.
Where, L.P.: Lone Pair B.P.: Bond Pair
Reason:
L.P. is attracted by the nucleus of single while bond pair is attracted by nuclei of two-atom. Thus, L.P. occupy more space around the central atom then bond pair.
- Triple bond causes more repulsion than double bond and double bond causes more repulsion than a single bond.
shape of molecules or ions:
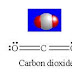
1. Electron Pair = 2
With zero L.P.: Shape: Linear
Bond angle:180⁰
Example: Carbon Dioxide
2. Electron Pair = 3
case 1
With zero L.P.: Shape: Trigonal Planner
Bond angle : 120⁰
Example: BF₃
 |
| BF₃ |
case 2
With one L.P.: Shape: V-Shape
Bond Angle:<120⁰
Example: SO₂
3. Electron pair=4
case 1
With zero L.P.: Shape: Tetrahedral
Bond angle: 109.5
Example: CH₄
 |
| CH₄ |
case 2
With one L.P.: Shape: Pyramidal
Bond angle: <109.5
Example: NH₃
case 3
With two L.P.: Shape: V-Shape
Bond angle: <109.5
Example: H₂O
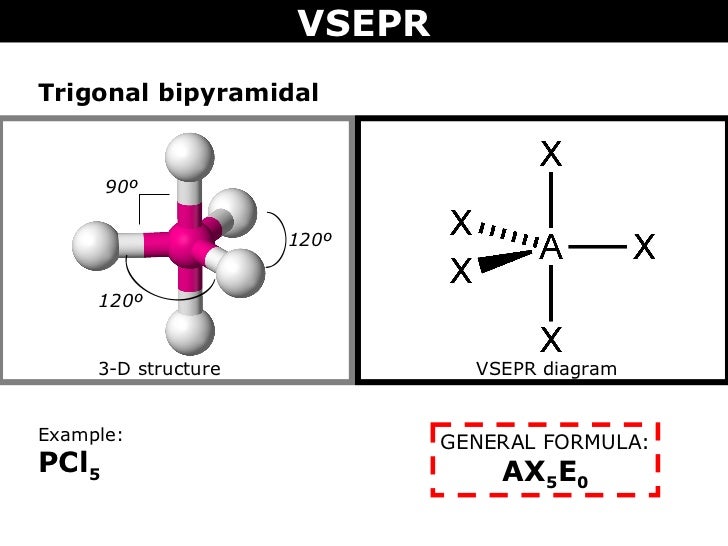
4.Electron pair=5
case 1
With zero L.P.: Shape: Trigonal Bipyramidal
Bond angle:
Example: PCl₅
case 2
With one L.P.: Shape: See-Saw
Bond angle: <120 , <90
Example: SF₄
case 3
With two L.P.: Shape: T-Shape
Bond angle: <90
Example: ClF₃
case 4
With three L.P.: Shape: Linear
Bond angle: 180
Example: XeF₂
Blent's rule
When all surrounding atoms attached to the central atom through a single covalent bond than more electronegative atom prefer to stay at the axial position and other atoms prefer to stay at the equatorial position. Bond length of atoms at the axial position is greater than that of atoms at the equatorial position.
5.Electron pair=6
case 1
With zero L.P.: Shape: Square bipyramidal
Bond angle:90
Example: SF₆
case 2
With one L.P.: Shape: Square Pyramidal
Bond angle:
Example: XeOF₄
case 3
With two L.P.: Shape: Pentagonal Bipiramidal
Bond angle: 90
Example: XeF₄
6.Electron pair=7
case 1
With zero L.P.: Shape: Pentagonal bipyramidal
Example: IF₇
case 2
With one L.P.: Shape: Distorted Octahedral
Example: XeF₆















No comments:
Post a Comment